SIMPLIFY E-INVOICE WITH GOLDSOFT
Phase 3 of e-Invoicing Has Started

We're thrilled to announce that Goldsoft is now an Accredited Peppol Ready Service Provider (PRSP) and Service Provider (SP) for e-invoicing!
This milestone reinforces our commitment to helping businesses ensure regulatory compliance and streamline their invoicing processes.
What is e-Invoicing?
e-Invoicing is the electronic exchange of invoices between businesses and government entities. The Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (LHDN) is mandating e-Invoicing for all commercial taxpayers in Malaysia to streamline processes and enhance efficiency.
Why Choose Goldsoft for Malaysia e-Invoicing?
With 28 years of experience in ERP and accounting solutions for Malaysia's retail and trading distribution, and successful GST and SST compliance, Goldsoft is poised to guide businesses through e-Invoicing.
Malaysia e-Invoice Implementation Date
| Group | Implementation Date | Targeted Businesses Annual Turnover/ Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 August 2024 | > RM 100 million |
| 2 | 1 January 2025 | > RM 25 million and up to RM 100 million |
| 3 | 1 July 2025 | > RM 5 million and up to RM 25 million |
| 4 | 1 January 2026 | > RM 1 million and up to RM 5 million |
| 5 | 1 July 2026 | up to RM 1 million |
Taxpayers with an annual turnover or revenue of less than RM500,000 are exempted from implementing e-invoice.
Types of e-Invoice To Be Issued in Malaysia
The Malaysia e-invoice system includes several types of e-invoices, such as invoices, credit notes, debit notes, refund e-invoices, and self-billed e-invoices. Each type serves a specific purpose in electronically documenting transactions.
Standard e-Invoice
A detailed transaction record between a supplier and buyer.
Refund e-Invoice
To acknowledge customer returns and specify the refunded amount.
Credit Note
To adjust the amount owed due to returns, discounts, incorrect amounts delivered, or other discrepancies.
Debit Note
To adjust the originally agreed-upon total, for example, for additional customer services or incurred extra costs.
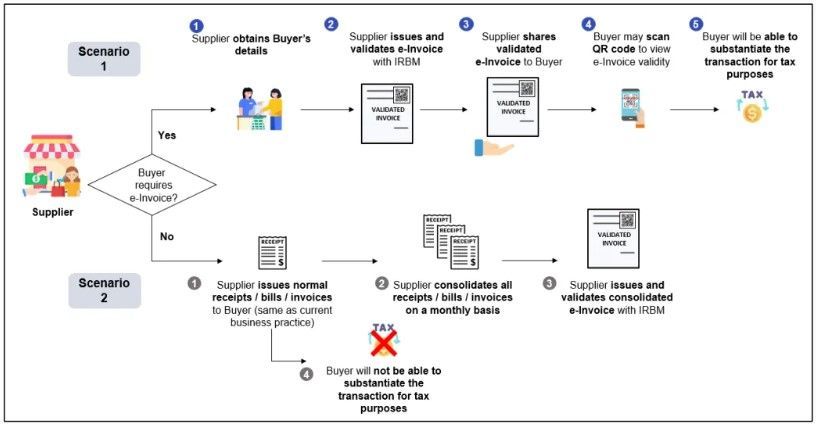
Overview of The e-Invoicing Process in Malaysia
There are two scenarios: where the customer requires an e-invoice and where the customer does not require an e-invoice.
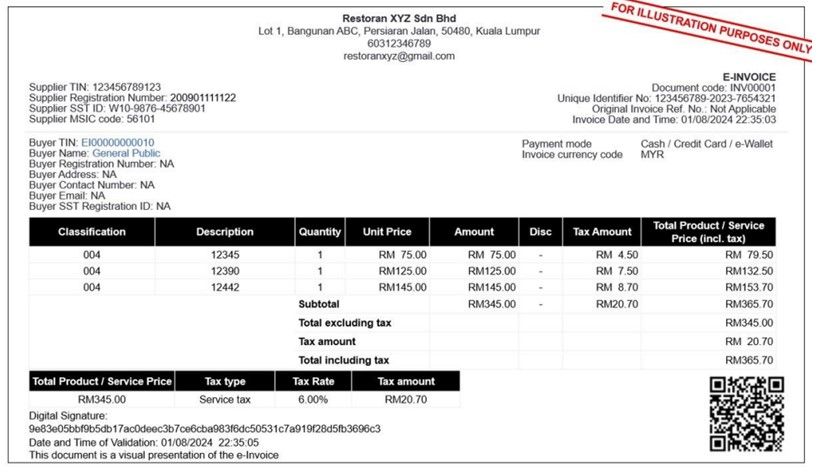
Example of Validated e-Invoices
The following is an example of an Malaysia's LHDN validated e-invoice in the specified XML or JSON format. The required data fields include 36 mandatory and 19 optional fields, totaling 55 data fields, in compliance with the e-invoice guideline version 2.3, published on April 6, 2024.
Image source: e-Invoice Specific Guideline (version 1.0) 29 September 2023
How to Prepare for e-Invoice Implementation in Malaysia?
e-Invoicing will become mandatory for all Malaysia's taxpayers regardless of sales threshold from January 2027. We would encourage taxpayers to conduct meetings with your key stakeholders and team members before making a decision on a solution that best fits your purpose.
1. Understanding Regulatory Requirements:
Familiarize yourself with the
e-invoicing regulations and standards set forth by
LHDN Malaysia, ensuring compliance with all legal obligations.
2. Assessment of Current Systems:
Evaluate your existing invoicing systems and processes to identify areas that may need adjustment or upgrade to accommodate e-invoicing requirements.
3. Selection of e-Invoicing Solution:
Select an e-invoicing solution aligning with your needs, considering integration capabilities, scalability, and compliance features. Assess current system compatibility and potential enhancements or integration with other middleware/software.
4. Vendor Collaboration and Support
Collaborate closely with your chosen e-invoicing vendor to leverage their expertise and support throughout the implementation process, ensuring successful deployment and ongoing maintenance.
Goldsoft e-Invoicing Solutions
Goldsoft e-Invoice Ready
ERP Solution
(Direct Integration of Goldsoft ERP with MyInvois System)
- Ideal for retail and trading distribution companies.
- e-Invoices are generated in Goldsoft's ERP system and sent directly to the LHDN MyInvois System without human intervention.
- Clients able to track and monitor e-invoice submissions, validation, and statuses in real-time via e-invoice dashboard.
Goldsoft e-Invoice
Middleware Solution
(Integration of Client's system with MyInvois System)
- Ideal for companies looking to streamline e-invoicing processes.
- Enable your company to send e-invoices, using your existing ERP/accounting software,
- Goldsoft as a service provider to convert documents (SFTP/ API/ Batch File Upload) to standard specifications and send it to LHDN.
- Clients able to track and monitor e-invoice submissions, validation, and statuses in real-time via e-invoice dashboard.
Why Choose Goldsoft for your e-Invoicing Needs?
Discover the benefits of e-invoicing with Goldsoft solutions
Integration to LHDN
Experience effortless integration between Goldsoft's e-invoicing solution and the Malaysia's LHDN MyInvois System, ensuring smooth data transmission and compliance with LHDN regulations.
e-Invoice Efficiency
Enjoy streamlined invoice generation, data validation, and real-time tracking of e-invoice statuses, resulting in increased operational efficiency and reduced manual errors.
28 Years of Reliable Experience
Benefit from a experienced ERP solution provider with dedicated customer assistance from Goldsoft, ensuring a smooth implementation process and ongoing assistance for any inquiries or issues that may arise.
Data Security
Goldsoft e-Invoicing prioritizes the security of your financial data, employing industry-standard encryption, secure cloud infrastructure, and stringent access controls to safeguard sensitive information.
GET IN TOUCH
We'll explore your requirements and discuss the specifics needed for you to achieve e-invoice Malaysia compliance.